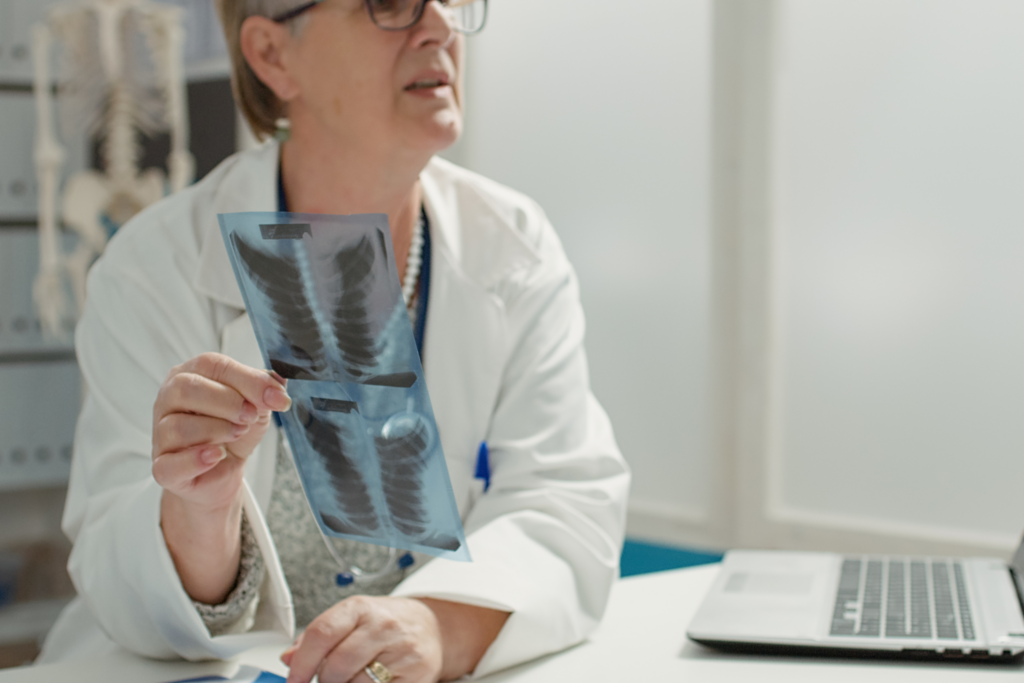
Lung cancer is a formidable adversary, affecting millions of lives around the world. As a thoracic oncology surgeon, I’ve witnessed the impact of this disease firsthand, and I understand the importance of providing comprehensive information to empower individuals and families facing a lung cancer diagnosis. In this detailed blog post, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of lung cancer, from its causes and risk factors to the latest advancements in treatment options.
What is Lung Cancer?
The lungs are vital organs responsible for the exchange of gases during breathing. However, cancer can strike when cells lose control of the cell division cycle, multiplying rapidly and forming tumors within the lungs. Lung cancer is one of the deadliest forms of cancer and can spread throughout the entire organ. Smoking remains a significant risk factor, but there is a concerning rise in non-smoking-related cases, particularly in India. Annual lung cancer screening is recommended to assess respiratory health.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
In the early stages, lung cancer often remains silent, with symptoms appearing only as the disease progresses. Lung cancer symptoms may include:
A persistent, unrelenting cough
Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Hoarseness
Unexplained weight loss
Bone pain
Headache
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional when any of these symptoms are observed.
Causes of Lung Cancer
Cigarette smoke contains carcinogens that damage lung cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth. This damage can occur quickly, overwhelming the body’s natural repair mechanisms. Additional risk factors include:
Exposure to secondhand smoke
Previous radiation therapy
Exposure to radon gas
Occupational exposure to carcinogens like asbestos
Family history of lung cancer
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer can be categorized into two major groups based on microscopic examination of lung cells:
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
Predominantly seen in heavy smokers.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Encompasses various subtypes, including squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Risk Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can be altered to reduce the risk of lung cancer, but others, like genetics, are beyond control. Key risk factors include smoking, secondhand smoke exposure, radiation therapy, radon exposure, asbestos exposure, and a family history of lung cancer.
Complications
Lung cancer can lead to various complications, including shortness of breath, coughing up blood, pain, and metastasis—the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body via the bloodstream.
Staging of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is staged to determine the extent of the disease. The stages are:
- Stage I: Cancer is small and limited to one area of the lung.
Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or invaded nearby structures.
Stage III: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the middle of the chest, called mediastinal lymph nodes.
Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Investigation and Lung Cancer Screening
Screening for lung cancer involves comprehensive testing, including a low-dose CT scan of the thorax and lung function assessments. Various imaging tests, such as chest X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and PET CT scans, aid in diagnosis. Sputum cytology and tissue sample (biopsy) procedures help identify cancer cells, while mediastinoscopy and needle biopsies assist in staging and determining the type and severity of lung cancer.
Treatments
Lung cancer treatments are tailored to each patient’s unique situation:
Surgery
Procedures like wedge resection, segmental resection, lobectomy, and pneumonectomy aim to remove cancerous tissue from the lungs.
Radiation Therapy
High-energy radiation targets and destroys cancer cells and may be combined with chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
Medications kill cancer cells and can be used alongside radiation therapy.
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
Precise beams of energy are directed at tumors, often used for small lung cancers or metastatic lesions.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Medications block internal cell damage, particularly for advanced or recurrent cancer.
Immunotherapy
Drugs impede protein production in cancer cells, harnessing the immune system to combat cancer.
Palliative Care
Specialized care minimizes discomfort, improves quality of life, and enhances mood.
Conclusion
Understanding lung cancer is vital in the fight against this formidable disease. Knowledge, early detection, and personalized treatment plans are powerful tools in the battle against lung cancer. Consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best options for your specific case. Together, we can work towards better outcomes and an improved quality of life for those facing lung cancer.
Lung and Trachea
- Lung Cancer
- Tracheal Disease
- Infective Lung Disease
- Non Infective Lung Disease
- Biopsy
Pleural and Mediastinum
- Mediastinal Cancer
- Thymic Cancer and Thymoma
- Myasthenia Gravis
- Pneumothorax
- Pleural Effusion Drainage
- Chylothorax Management
- Pericardial Disease
- Intra Pleural Heated Chemotherapy
Chest wall and Diaphragm
- Pectus Deformity
- Rib Fracture Repair
- Diaphragm Disorder
- Hyperhidrosis Treatment
- Chestwall Reconstruction
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
Key Hole Surgeries
- Video-assisted Thorracoscopic Surgery
- Robotic-assisted Thorracoscopic Surgery
Inhalesexhales.clinic@gmail.com
drrajkamalvishnu@gmail.com
Inhales Exhales Clinic
No 41 , 1st Main Road, Jawahar Nagar, Chennai 600082